Engineering X Y Z Axis . It follows the rule that x x y = z. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the direction of motion. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. the y axis refers to vertical position (perpendicular to the base) and the x axis refers to the horizontal position (parallel to the base). to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane.
from stock.adobe.com
It follows the rule that x x y = z. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane. the y axis refers to vertical position (perpendicular to the base) and the x axis refers to the horizontal position (parallel to the base). The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the direction of motion.
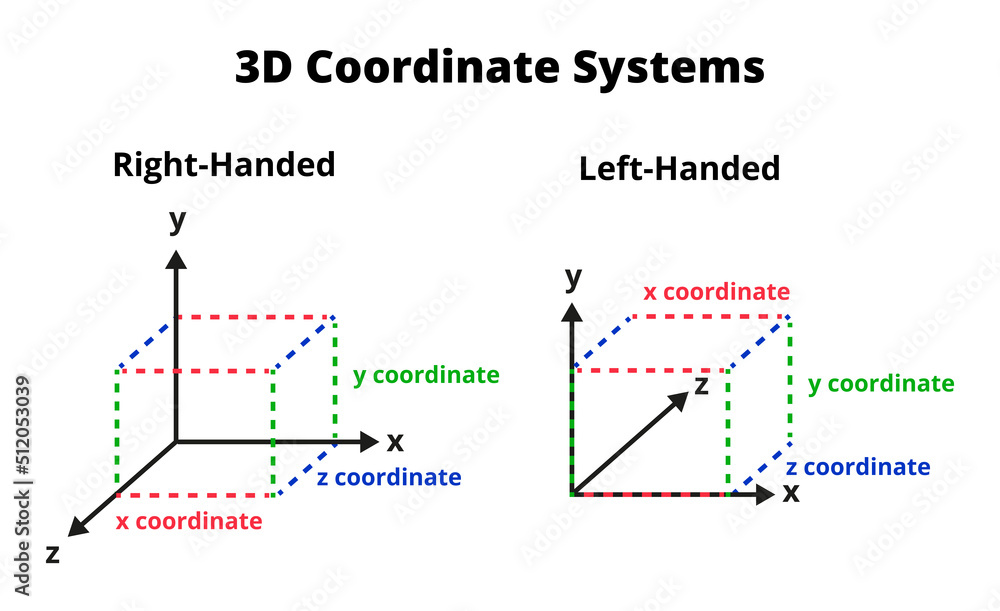
3D coordinate systems, righthanded and lefthanded. 3D cartesian
Engineering X Y Z Axis to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: It follows the rule that x x y = z. to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane. the y axis refers to vertical position (perpendicular to the base) and the x axis refers to the horizontal position (parallel to the base). The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the direction of motion.
From mammothmemory.net
Graphs showing a 3 dimensional shape will have a Z axis Engineering X Y Z Axis The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the direction of motion. The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.researchgate.net
Rotation about z axis by an angle ϕ. The new x, y and z axes are called Engineering X Y Z Axis to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.machinistguides.com
X, Y, & Z CNC Codes Explained An Easy Intro for Beginners [Coordinates Engineering X Y Z Axis The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane. the y axis refers to vertical position (perpendicular to the base) and the x axis refers to the horizontal position (parallel to the base). It follows the rule that x x y = z. The two axes of the horizontal plane. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.geogebra.org
Angles between a Vector and the Axes GeoGebra Engineering X Y Z Axis to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: It follows the rule that x x y = z. the y axis refers to vertical position (perpendicular to the base) and the x axis refers to the horizontal position (parallel to the base). to specify the location of. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
X Y And Z Axis Engineering X Y Z Axis the y axis refers to vertical position (perpendicular to the base) and the x axis refers to the horizontal position (parallel to the base). It follows the rule that x x y = z. to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: to specify the location of. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From stock.adobe.com
3D coordinate systems, righthanded and lefthanded. 3D cartesian Engineering X Y Z Axis to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: It follows the rule that x x y = z. The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From holtagon1963.blogspot.com
How to Draw a Plane on the Z Axis Holt Agon1963 Engineering X Y Z Axis The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the direction of motion. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From socratic.org
What is a zcoordinate? Socratic Engineering X Y Z Axis The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the direction of motion. It follows the rule that x x y = z. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.codeproject.com
Kinect Joint Rotation The Definitive Guide CodeProject Engineering X Y Z Axis the y axis refers to vertical position (perpendicular to the base) and the x axis refers to the horizontal position (parallel to the base). It follows the rule that x x y = z. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.youtube.com
Part 2 Calibrate X Y Z axis made easy Wanhao D9 and other 3d printer Engineering X Y Z Axis to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: It follows the rule that x x y = z. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the direction of motion. The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From dxoxbkmif.blob.core.windows.net
Xyz Axis Definition at Betty Cohen blog Engineering X Y Z Axis It follows the rule that x x y = z. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.youtube.com
The xyz Coordinate System YouTube Engineering X Y Z Axis to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From gis.stackexchange.com
Inserting XYZ axis in ArcGIS Pro? Geographic Information Systems Engineering X Y Z Axis The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane. It follows the rule that x x y = z. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.researchgate.net
The XYZcoordinate system. In this coordinate system, the viewing Engineering X Y Z Axis It follows the rule that x x y = z. to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From exodhntor.blob.core.windows.net
How To Find Z From X And Y at Heidi blog Engineering X Y Z Axis It follows the rule that x x y = z. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and y, with the x axis being in the direction of motion. to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: the y axis refers to vertical. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.istockphoto.com
Xyz Axis Illustrations, RoyaltyFree Vector Graphics & Clip Art iStock Engineering X Y Z Axis to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. It follows the rule that x x y = z. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.researchgate.net
Movement in coordinate axes X, Y and Z Download Scientific Diagram Engineering X Y Z Axis to specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane. to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: It follows. Engineering X Y Z Axis.
From www.youtube.com
Angle a Vector makes with the x, y, and zaxes YouTube Engineering X Y Z Axis It follows the rule that x x y = z. to define roll, pitch, and yaw in linear systems, we first need to establish the three primary axes: The y axis is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the direction of motion and is also in the horizontal plane. The two axes of the horizontal plane are typically defined as x and. Engineering X Y Z Axis.